by Sam Bower 2013

Standing in the woods near the pond at the Schuylkill Center, we can look out and see a range of time scales. The brown and golden leaves under our feet from the Fall- the leftovers of a year’s work by the trees above us. Perhaps there’s snow still on the ground from a recent storm, itself the result of the vast cycles of evaporation off the ground and from lakes and oceans into the atmosphere and clouds and back down again. Some of the trees around us are decades, maybe hundreds of years old. Frogs and fish and insects hidden underground or inside vegetation, birds in their nests chirping and flitting about, grasses, flowers each have their lifespans and carefully timed cycles to support, prey on or evade each other – evolved over thousands, even millions of years.

Changing urban land use patterns offer opportunities for shifts in paradigm, innovation and art: (http://www.takebackthetract.com/)
When we think of culture and public art, we have an opportunity to think along similar time scales. Humans also have their cycles of productivity, lifespans and fleeting passions. These interests also evolve over time to reflect our knowledge, context and the resources at hand.
Sometimes an artwork arrives with a bang and loud trumpets and just as quickly fades into the day or week or month only to live on in memory and documentation. Like sighting a rare Blue-winged Warbler in the forest, or waking up to an overnight dusting of snow that makes the line of every tree suddenly visible, or the miracle of a drop of dew on a leaf in the Summer that reflects a world upside down, these brief events delight and remind us of the preciousness of the present moment. Some things are simply best communicated ephemerally. A song. A performance. A rain shadow.
On the medium scale, we have most plants and animals and planted crops and, alas, most human projects. We tend to think in terms of months or years or at best decades. A hundred years without regular maintenance is long for a built structure, long for most outdoor sculptures, too, even those meant to be “permanent”. It’s the lifespan of an exhibition, a person, a raven, a grove of Sassafrass (albidum) and it serves to ground us in the familiar. We can see it and know it because it’s us. Within a century, with the strategic accumulation of such medium scale projects, we can make major improvements or changes to a place and set things in motion that can last a lot longer.
It’s the larger time frame that gets the least attention and is often more difficult to wrap our heads around. The scope of generations. Climate change. Geological time. Too often, these big shifts elude us. We claim not to know. A sudden revolution or a storm or an accident can thwart the best laid plans. Ultimately, we know that a focus on the specific is often too limiting a scale for something long lived and significant.
At the Schuylkill Center, the increasing flow of voracious and unmanaged deer over and across the land, and the invasive Asian earthworms (Amythas hilgendorfi and agrestis) under it, are regional and even continental challenges. To encourage specific changes here, we would need to plan and coordinate with those working within much larger areas to be effective. To set in motion a resilient set of processes that truly begin to nudge us and the natural areas under our trust towards a future that can address a world in flux is an enormous challenge. At a time of massive species extinction and global changes in climate, we need a flexible and directed multi-timescale approach to culture and ecological stewardship.
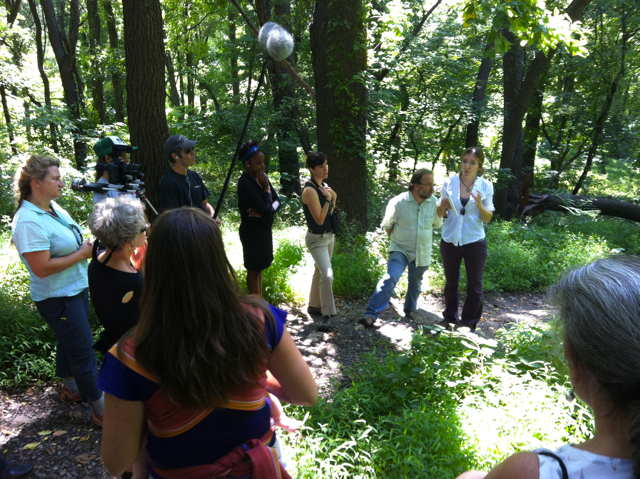

The environmental art advisory team at the Schuylkill Center in 2012.
This is the challenge ahead for the Schuylkill Center. Most art, even ecological art is a flash in the pan, a tasty snack. They generate attractive catalogs and press releases and perhaps valuable discussion, but will the worms and watersheds really notice? We have large institutions for pickling great paintings and sculptures, but outdoor work designed to heal the earth and support our communities is a different animal. While a project can have representative images and installations at these museums (usually as part of a temporary exhibition), the real work gets done on the ground and in context.
Like in an ecosystem, we need the dew drops and temporary projects to delight and attract. We also require specific medium term artful initiatives to control erosion, channel rainwater, educate people longer term and connect current and future generations to the land. It falls to the long term, multi-generational projects, however, to provide a long term vision that considers the implications and resilience needed to cope with, say, a 2-6 degree rise in global temperatures over the next few hundred years. It seems we’d want to look at rising water levels – how would this affect the Schuylkill River? What local conditions will we need to ensure maximum biodiversity and habitat support for migrating species seeking more favorable habitats?
In nature, we can see the extraordinary interplay of finely tuned life cycles working together to support the system as a whole. As these delicately synchronized dances grow increasingly out of synch with pollution, temperature and weather changes, what we know and have studied over the past hundreds of years will require new interpretation. It will become less about restoration of past conditions and more about our capacity to surf these changes. Our notion of what art is will also need to change.
For ecological art to be effective, we will need to think along multiple time scales and beyond the individual artwork, towards a future-oriented cultural system as a whole. How can the brief delightful moments support the larger arc of history? Can we begin to layer and combine artworks to support each other, much like the shift from unicellular to multi-cellular life? I’m looking forward to the role the Schuylkill Center can play in this civilizational shift. It is a precious opportunity to contribute to our times and help develop new cultural patterns for generations to come.
©Sam Bower 2013